
having more data points in the set) does not always improve the accuracy of the interpolation. It is important to keep in mind, because it means that going to higher degrees (i.e.

It is a problem of oscillation at the edges of an interval when using polynomials of high degree over a set of equidistant interpolation points. Note that Lagrange's interpolation formula is susceptible to Runge's phenomenon. Which means that the Lagrange polynomial interpolates the function exactly. If you look at the formula of the basis polynomial for any j, you can find that for all points i not equal to j the basis polynomial for j is zero, and in point j the basis polynomial for j is one.
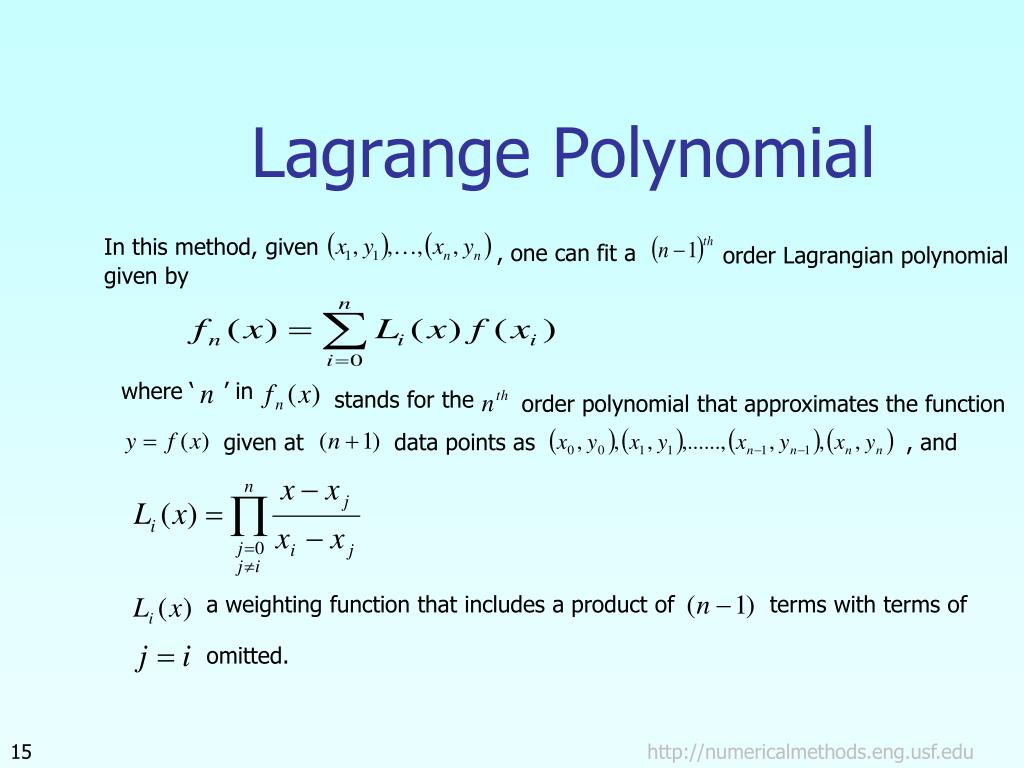
Let's construct the following polynomial (called the Lagrange polynomial): Let's suppose we have a set of data points for the unknown function, where no two x are the same: You can also find some theory about the Lagrange polynomial below the calculator. The chart at the bottom shows the Lagrange polynomial, as well as its basis polynomials.

If you want to see a step-by-step solution for the polynomial formula, turn on the "Show Step-By-Step Solution" option. If you want to interpolate the function by the Lagrange polynomial, enter the points of interpolation into the next field, just x values, separated by spaces.īy default, the calculator shows the final formula and interpolated points. It plots the data set, interpolated points, Lagrange polynomial and its basis polynomials on the chart.įirst, enter the data points, one point per line, in the form x f(x), separated by spaces.It interpolates the unknown function by computing the value of the Lagrange polynomial at the given x values (points of interpolation).It shows step-by-step formula derivation.It finds the final Lagrange polynomial formula for a given data set.The calculator below can assist with the following: In these problems you are often asked to interpolate the value of the unknown function corresponding to a certain x value, using Lagrange's interpolation formula from the given set of data, that is, a set of points x, f(x). I wrote this calculator to be able to verify solutions for Lagrange's interpolation problems.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
